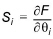
Local sensitivity analysis provides the sensitivity of the model parameters around a specified parameter set, and hence gives information about the importance of the parameters only at that location in parameter space. If the simulation model is highly non-linear in its parameter-output interaction, sensitivity measures may vary considerably in the parameter space. Thus, parameters that are insensitive for certain parameter sets may be highly sensitive for other parameter sets and vice versa.
The local sensitivity measures are calculated around the initial parameter set specified on the Model Parameters page.
Difference approximation
The sensitivity of a parameter with respect to a model response (output measure) is defined as
(1.15) 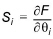
where F is the output measure, and qi is the considered model parameter. The sensitivity measure is evaluated around a specified parameter set (q1,q2,..,qn).
In AutoCal a finite difference approximation is used to evaluate the sensitivity coefficients. Three different options are available:
Forward difference approximation:
(1.16) 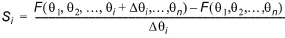
Backward difference approximation:
(1.17) 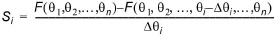
Central difference approximation:
(1.18) 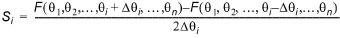
where Dqi is the parameter perturbation.
The calculation of the sensitivity coefficients require n + 1 model evaluations in the case of forward and backward difference approximations, and 2n +1 model evaluations when the central difference approximation is applied.
Perturbation option
The parameter perturbation can be calculated as:
A fraction of the initial parameter value:
(1.19) 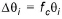
A fraction of the parameter interval:
(1.20) 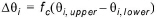
where qi,upper and qi,lower are the specified upper and lower limits of the parameter.
Perturbation fraction
The perturbation fraction is the fraction fc of the initial parameter value or the parameter interval depending on the choice of parameter perturbation.
Calculate covariance matrix
If this option is selected, the covariance matrix of the parameters evaluated around the initial parameter set is calculated. This matrix is derived based on the sensitivities of the simulated values corresponding to each of the target values with respect to each of the parameters. The matrix can only be calculated in the case a weighted least squares aggregated objective function is specified, i.e. each Output measure on the Objective Functions page is defined as a RMSE statistic, each Objective function is defined as a Weighted sum of squares, and the Aggregation of objective functions is set to No transformation.