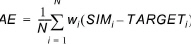
Name
Name of the output measure.
Output file and item name
File name and corresponding item name of the time series of the simulation results.
Target file and item name
File name and corresponding item name of the target time series.
Statistic type
AutoCal includes three basic comparison statistics:
Average error (Avg. Error):
(1.1) 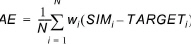
Root mean square error (RMSE):
(1.2) 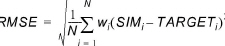
Standard deviation of residuals (St.Dev.):
(1.3) 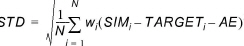
where TARGETi and SIMi, i = 1,..,N are the observed and the corresponding simulated time series, respectively, and wi is a user specified weight (weight below and weight above). Before calculation of the statistics, the time series are synchronised; that is, simulated values are extracted at the same time instants as the available target values using linear interpolation.
The three statistics are linked via the equation:
(1.4) 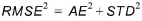
The statistic AE is a measure of the general offset between targets and simulations (bias), whereas STD is a measure of the dynamical correspondence. RMSE is an aggregated measure that includes both bias and dynamical correspondence.
Besides the basic statistics, AutoCal includes two event-based statistics:
Error of maximum value (Error of max.):
(1.5) 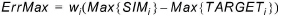
Error of minimum value (Error of min.):
(1.6) 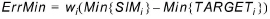
The maximum and minimum target and simulated values are extracted in the period defined in the target file.
Weight below and weight above
The weight below is the weight assigned when the simulated value is below the target, and the weight above is the weight assigned when the simulated value is above the target. The weights should reflect the relative importance of positive and negative deviations from the target. In addition, the weights should specify the relative importance of the different output measures. For instance, in the model calibration, the assigned weights should reflect the measurement uncertainties, and the correlation between the measurements. That is, smaller weights should be given to more uncertain measurements, and if clusters of measurement points exist, these points should be given a lower weight than single point measurements in other parts of the modelling domain in order not to put undue emphasis on model performance in certain areas.
Function name
The function name of the objective function in which the output measure should be included. In the drop-down menu the function names from the Objective functions table are given.