The Basin modules includes specification of Basin specific features and Global parameters for the project:. Options are:
– Include groundwater (add-on for Basin Simulation)
– Include reservoir sedimentation (add-on for Basin Simulation)
– Water quality (add-on for Basin Simulation)
– Use global ranking (add-on for Basin Simulation)
– Unlimited resources in catchments without groundwater model
– Subtract area of irrigation users and reservoirs from catchment area to calculate runoff
Rainfall runoff
Basin simulation
Global parameters
Optionally, rainfall-runoff modelling can be included in the Basin model.
Inclusion of Rainfall runoff in a simulation requires that one or more Catchments are defined in the Basin model. Runoff from catchments to river nodes can then either be included through the use of fixed runoff time series files for individual catchments or by activating the calculation of runoff from Catchment characteristics and precipitation (rainfall).
Two types of rainfall-runoff models are available:
· NAM:
A lumped, conceptual rainfall-runoff model, simulating the overland flow, interflow, and baseflow components as a function of the moisture contents in four storages.
· UHM:
The Unit Hydrograph Model includes different loss models (constant, proportional) and the SCS method for estimating storm runoff.
The type of model and associated required input data are specified in Catchment definitions page (cf. Section 7.1.3).
Basin simulation includes the options for calculating a large variety of different processes and model components taking part in the water consumption and influencing the water balance with a river basin. Basin simulation utilise the calculation engine from DHI’s predecessor to MIKE HYDRO for water resources management simulations; MIKE BASIN, and most of the calculation methods for specific modelling features are therefore mature and validated through intensive project applications over a large period of time.
Optionally, groundwater processes can be included in Basin module. The underlying conceptual model is the linear reservoir model concept (see Appendix A.1 The Linear Reservoir model) with one or two aquifers (fast/slow response).
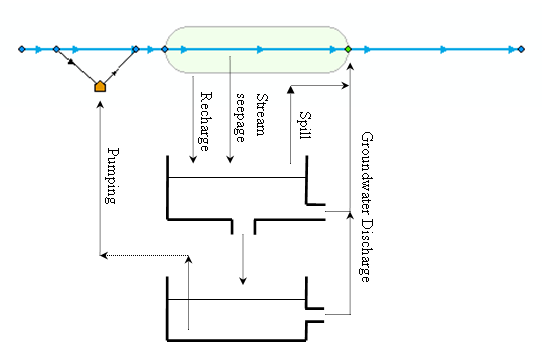
The conceptual structure of the two-layer groundwater component is illustrated in Figure 4.2. Single-layer models only include the shallow (upper) aquifer.

Figure 4.2 Conceptual structure of the groundwater component
As illustrated in Figure 4.2 groundwater interacts with the surface water via groundwater recharge, groundwater discharge and seepage from rivers, reservoirs and connections. Moreover, when the water table of the shallow (upper) aquifer reaches the land-surface, it starts to spill directly into the river. Finally, groundwater from the deep aquifer can be pumped by water users.
Include reservoir sedimentation
The reservoir sedimentation module routes sediment through the river network and calculates the potential deposits of sediment in the Reservoirs. The reservoir sedimentation module is not a sediment transport model. Sediment is supplied by catchments and is routed through the river network under the assumption that no erosion takes place and deposition solely occurs in the Reservoirs. Any sediment not deposited in the Reservoir is routed to the river downstream and to users supplied by the Reservoir. Sediment is distributed according to the discharge distribution.
The Water quality (WQ) module is based on MIKE ECO Lab, which is a highly flexible framework for defining water quality models. MIKE ECO Lab utilise a concept of templates where water quality models are defined with equations and variables, and the water quality option therefore, allows the usage of different water quality models/templates depending on the issue of concern. MIKE HYDRO Basin installation includes two predefined water quality templates that can be applied as is - or can be adjusted by the user to conform with the specific project requirements.
Global ranking may be used to prioritise water allocation to Water users, Hydropower plants and Reservoirs independently of their geographical location in the river basin. When global ranking is selected, all other allocation rules/priorities are ignored. This includes local priorities and Reservoir reduction levels.
The Global parameters defines global characteristics in the model framework which will be globally applied (for all relevant features).
Unlimited resources in catchments without groundwater model
If this parameter is enabled, groundwater in Catchments without a groundwater model is assumed to be an unlimited resource with no feedback to the surface water system. If it is disabled, no groundwater is available in Catchments without groundwater model.
Subtract area of irrigation users and reservoirs from catchment area to calculate runoff
If this module/parameter is enabled, the area of irrigation users and reservoirs is subtracted from the catchment area prior to calculating catchment runoff. This is particularly important if irrigation users and/or reservoirs have significant surface areas compared to the catchment area, in which they are located.