 . A new line appears in the window displayed at the bottom of the screen. A Name should be specified by for the crop type. The inputs related to the crop of interest can be entered in the boxes of the Crops section.
. A new line appears in the window displayed at the bottom of the screen. A Name should be specified by for the crop type. The inputs related to the crop of interest can be entered in the boxes of the Crops section.
Given the soil moisture content and reference evapotranspiration, the crop module takes the input to calculate the corresponding crop evapotranspiration and soil evaporation.
To create a new model click on the ‘Append’ button, designated with the symbol  . A new line appears in the window displayed at the bottom of the screen. A Name should be specified by for the crop type. The inputs related to the crop of interest can be entered in the boxes of the Crops section.
. A new line appears in the window displayed at the bottom of the screen. A Name should be specified by for the crop type. The inputs related to the crop of interest can be entered in the boxes of the Crops section.
Alternatively, predefined crop models can be loaded from a template file by on the ‘Load template’ button,  , and browsing to the specific template file. An existing template used in another MIKE HYDRO model can also be used, by clicking on ‘Import existing’,
, and browsing to the specific template file. An existing template used in another MIKE HYDRO model can also be used, by clicking on ‘Import existing’,  , and browsing to the previously created .mhydro file.
, and browsing to the previously created .mhydro file.
To delete the currently displayed crop type information click on ‘Delete’:  .
.
To switch between the different Crops models, click on the lines relative to different crop types in the tab in the lower part of the Tabular view.
Two different Crop model types are currently available:
· FAO 56 DualCropCoefficient model
Two different Crop model types are currently available:
· FAO 56 DualCropCoefficient model
FAO 56 DualCropCoefficient model
The FAO 56 method is based on the dual crop coefficient method described in FAO 56. The FAO 56 DualCropCoefficient model calculates the transpiration and soil evaporation separately and thus allows for a more accurate quantification of the consequences of using different irrigation technologies.
Following the FAO 56 terms, the Crop stages are divided into the following:
· Initial
· Development
· Mid season
· Late season
The parameters to be assigned to each Crop stage are:
· Length. The length, in days, of the specific period.
· Kcb. For each stage, a so-called basal crop coefficient (Kcb) is assigned. The basal crop coefficient is defined as the ratio of the crop evapotranspiration over the reference evapotranspiration (ETc/ET0) when the soil surface is dry but transpiration is occurring at potential rate. Kcb is assumed constant in the initial and middle stages, and assumed to follow a linear variation between the stages.
· Root depth. The Root depth R determines the maximum depth from which the crop can extract water. The minimum and maximum depth has to be specified. It is assumed that the maximum depth is obtained at the beginning of the middle stage, and that the variation between the initial depth and the maximum depth is determined by the following relationship:
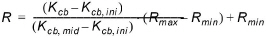
where:
Kcb,ini : Initial crop basal coefficient [-]
Kcb,mid : Basal crop coefficient in middle stage [-]
Rmax : Maximum root depth [m]
Rmin : Minimum root depth [m]
· Max height. The influence of the vegetation surface roughness on the evapotranspiration is taken into account through a climatic correction factor applied to the basal crop coefficient. The vegetation height is assumed to scale with the basal crop coefficients and is calculated as:
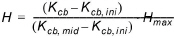
for the initial and development stage, after which the height is assumed to have reached its maximum (Hmax).
· Length (Yield). When the FAO 33 yield model is applied, each stage is assigned a length that may, but does not have to, be the same as the growth stages in the Crops model to which it is related.
· Ky. Yield response factor that must be specified when the FAO 33 yield model is applied. A crop is usually sensitive with different intensities to soil moisture stress at different stages of its development.
For the Rice Crop model, one additional stage has been included: the Nursery phase. This stage is the period in which the rice plants are developing before transplantation.
The supplementary inputs for the Nursery stage are:
· Length. In days.
· Nursery area. It is the ratio of the total field area in which Nursery takes place. This is usually a small part of the future rice field.
· Land preparation. The Land preparation stage is the period, expressed in [days], before transplanting (at the beginning of the Initial stage). During this period the land is irrigated and the soil is puddled.

Note: As the Nursery stage also covers the Land preparation, the Nursery period should be longer than the Land Preparation period.
Growing period
In this section two inputs should be specified:
· Sowing day/month. The starting date (sowing date) of the shift of the specific crop.
· Last irrigation day. The irrigation can be stopped after a specified day. This is a useful option when irrigation demand is calculated by the model.
Yield
· Depletion fraction. The depletion fraction p expresses the sensitivity of the crop to soil moisture stress, or more specifically, the fraction of the totally available water (TAW) at which soil moisture stress will start to reduce crop transpiration. The amount of water that may be depleted without stressing the plant is called the readily available water (RAW).
The relationship between RAW and TAW is:
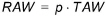
For soil moisture contents below RAW, transpiration is assumed to decrease linearly with soil moisture content and reach zero when the wilting point is reached (see Figure 8.4).
Figure 8.4 Relationship between RAW and TAW (after /1/)
Attaching a Yield model to a crop model allows the conversion of soil water stress into the corresponding yield loss, and hence, to quantify the costs of a soil moisture deficit.
One single yield model is currently available:
· FAO 33 Yield model
The following three options are available for the FAO 33 Yield model:
· Calculate yield. By ticking this box a yield model is attached to the crop model. When choosing this option, the Potential yield can be entered and so the Ky parameters for the different crop stages.
· Potential yield. This parameter, expressed in [kg/ha], represents the crop production per unit area of cultivated field and it must be entered when the yield model is included.
· Use yield stage length. Ticking this box enables the user to specify the length of the periods with different Ky in the Length (Yield) section. These may differ from the crop stage given in the Length section.

Note: The total length of the Length (Yield) periods has to be equal to the total length of the Length periods (without including Nursery).