
Developing a template
Creating and developing a MIKE ECO Lab template involves several steps.
1. Create a MIKE ECO Lab template
First you must create a MIKE ECO Lab template from the File/New menu or the New File icon. In both cases, you will chose MIKE Zero and then MIKE ECO Lab (.ecolab) in the New File dialogue. This will create a new blank MIKE ECO Lab template file.
Alternatively, you can copy and edit an existing MIKE ECO Lab template.
A few tips will be useful before you start.
· You should try to keep the names of the Constants, Forcings, etc. as short as practical. The names are used when defining Processes, Auxiliary Variables, and Derived Outputs.
· The names used in the definitions are case-sensitive.
· The names must be unique within the list of Constants, Forcings etc.
· To add a new Constant, Forcing, etc. right click on the item and chose the appropriate option.
2. Add State Variables to the Template
The only available State Variables are species concentrations. You must add one State Variable item for each Species in MIKE SHE that you want MIKE ECO Lab to modify during the WQ simulation.
The MIKE ECO Lab template must include at least one State Variable.

Note: The State Variable name must be exactly the same as the Species name in MIKE SHE.
The exception to the exact naming rule is when simulating Dual domain mass transfer. In this case, the State Variable name must use the reserved suffix "_2" for the solute in the secondary porosity. For example, OXYGEN and OXYGEN_2 would be the State Variable names for the species OXYGEN in MIKE SHE.
3. Add one or more Constants
Constants are spatially distributed values that are constant in time. Each constant is either pre-defined by the MIKE SHE setup (MIKE_SHE_SUPPLIED_CONSTANT), or it is User Defined in the MIKE SHE model. All other values will be ignored.
Pre-defined MIKE SHE Supplied Constants
If the Constant is defined by the MIKE SHE model setup, then the Built in ID must be MIKE_SHE_SUPPLIED_CONSTANT.
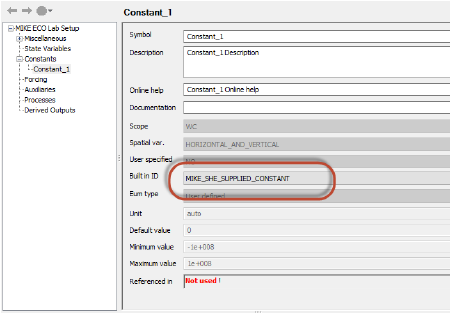
The available pre-defined MIKE SHE Supplied Constants are different depending on hydrological context (ie Overland Flow, UZ or SZ)..
|
Overland Flow |
Unsaturated Zone |
Saturated Zone |
|---|---|---|
|
Cell size |
Cell size |
Cell size |
|
Topography |
Cell volume |
Cell volume |
|
Detention storage |
Topography |
Topography |
|
|
Depth to cell top |
Depth to cell top |
|
|
Depth to cell bottom |
Depth to cell bottom |
|
|
Saturated water content |
Primary porosity |
|
|
Macropore porosity |
Secondary porosity |
|
|
Primary bulk density |
Primary bulk density |
|
|
Secondary bulk density |
Secondary bulk density |
The Symbol name that you define is carried over to the MIKE SHE list of Constants. In the MIKE SHE list of constants, you will define the actual value that will be supplied by MIKE SHE to MIKE ECO Lab.
User Defined Constants
If your Constant is not a pre-defined MIKE SHE constant, then you must define a value for the constant. In this case, you must define it as User Defined Constant.
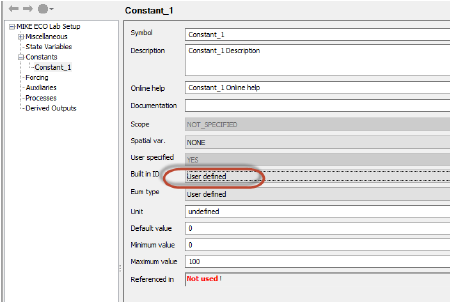
The actual values and spatial distribution of the Constant will be defined in the MIKE SHE Setup Editor. Any User defined Constants will be added to the list of constants under each of the domains (ie OL, UZ and SZ).
In the template, the only thing you need to specify is the name of the Constant. The name is then used when defining the Processes, Derived Outputs, etc.
If you have already defined the Constant in the Setup Editor, you may need to define it again in the list of Constants in the Setup Editor. This is most easily done by re-loading template with the browse button.
4. Add one or more Forcings
A Forcing is any spatially distributed value that is time varying. You can think of it as a value that is affecting the State Variable during the simulation. For example, air temperature will affect the degradation rate of a solute.
Similar to the Constants, each forcing is either pre-defined by the MIKE SHE setup (MIKE_SHE_SUPPLIED_FORCING), or it is User Defined in the MIKE SHE model. All other values will be ignored.
Pre-defined MIKE SHE Supplied Forcings
If the Constant is defined by the MIKE SHE model setup, then the Built in ID must be MIKE_SHE_SUPPLIED_FORCING.
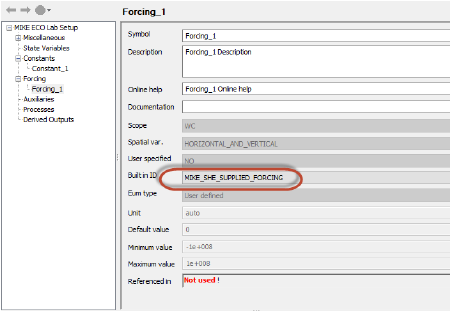
The available pre-defined MIKE SHE Supplied Forcings are different depending on hydrological context (ie Overland Flow, UZ or SZ)..
|
Overland Flow |
Unsaturated Zone |
Saturated Zone |
|---|---|---|
|
Time step length |
Time step length |
Time step length |
|
Precipitation rate |
Precipitation rate |
Precipitation rate |
|
Air temperature |
Air temperature |
Air temperature |
|
SW solar radiation |
SW solar radiation |
SW solar radiation |
|
Depth of overland water |
UZ Water content |
Depth to phreatic surface (positive)
|
|
Depth to phreatic surface (positive) |
Macropore water content |
SZ potential head |
|
SZ potential head |
Depth to phreatic surface (positive) |
SZ saturated thickness |
|
|
SZ potential head |
Soil temperature |
|
|
Soil temperature |
|
The Symbol name that you define is carried over to the MIKE SHE list of Forcings. In the MIKE SHE list of forcings, you will define the actual value that will be supplied by MIKE SHE to MIKE ECO Lab.

Note: The various other “MIKE_SHE_” forcings are used by MIKE Hydro River to define concentrations and mass of solute entering the river.
5. Create Auxiliary Variables, Processes and Derived Outputs
Auxiliary variables are used for intermediate calculations and must be defined as 3D (UZ and SZ) or 2D variables.
Processes transform a State Variable or calculate another result. Spatial variation and type must be defined for each process. Each process can be included in the results file by choosing "YES" in the "Output" box.
Derived Outputs allow the user to define output files based on the process results.