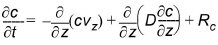
Governing Equations
For unsaturated solute transport in the soil matrix the advection-dispersion equation is
(33.17) 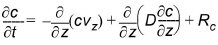
where c is the concentration of the solute, Rc is sum of sources and sinks, D is the dispersion coefficient, and vz is the vertical velocity.
The advective transport is determined by the water flux calculated during a MIKE SHE WM simulation. As the water flow is assumed strictly vertical, this restriction applies also to the advective transport of the dissolved solutes.
To determine the velocity, vz, the flux is divided by the moisture content:
(33.18) 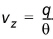
The mathematical formulation of the dispersion of the solutes follows the formulation derived for groundwater flow with a linear relation between the dispersion coefficient and the seepage velocity but limited to one dimension. In this case the dispersion coefficient can be written as:
(33.19) 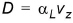
where aL is the longitudinal dispersivity of the porous medium which represents the heterogeneity of the soil hydraulic parameters. aL is allowed to vary vertically to account for different degrees of inhomogeneity in the soil. For unsaturated flow, the dispersivity is dependent on the water content, however, this relationship is neglected. .