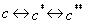
The three equilibrium sorption isotherms described so far can be extended to include kinetically controlled sorption. In the MIKE SHE AD module, a two-domain approach is used, where the sorption is assumed to be instantaneous for a fraction of the sorbed solute and rate-controlled for the remainder. A chemical formulation of this approach is given by:
(34.8) 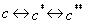
where c* is the amount of the solutes sorbed (described by the equilibrium sorption model), c** is the amount of the sorbed matter that is converted to the kinetically controlled sorption domain. Mathematically the work of Brusseau (1995) is implemented in MIKE SHE AD as
where K1 is the constant defining the rate of kinetic sorption. The formula is generalised so that effects of hysteresis can be taken into account, by specifying a K1 value for adsorption (c*>c**) and another value for desorption (c**>c*).
The formula is generally applicable for all the equilibrium sorption models. All constants appearing in the sorption models are assumed constant in time but may vary in space.