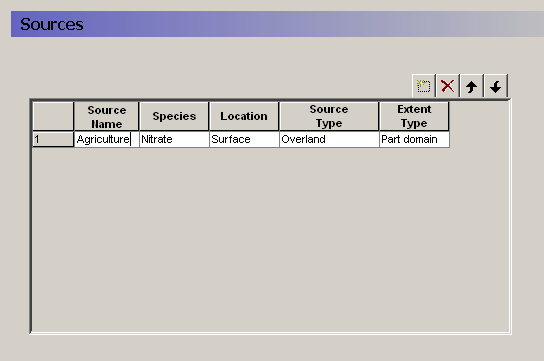

The specification of water quality sources is very flexible. The Sources dialogue allows you to add and delete sources, as well as define the type and location of the source. The table provides an overview of all of your sources in your model.
An important feature of the source location definition is the partial extent distribution function. This allows you to define, for example, a distributed global source file - say of the field scale agricultural inputs in your catchment - and run individual water quality scenarios for each sub-catchment (modelled as an partial extent) to assess the subcatchment contributions to the global stream impact.
Source Name - The name appears in the data tree for reference.
Species - You can only choose from the list of available species that you have defined in the Species (V1 p. 219) dialogue.
Location - The location is defines whether the source is located on the ground surface (Surface) or in the saturated or unsaturated zone (Subsurface). The available source types depend on where the source is located.
Source Type - If the source is located on the ground surface, then it can be either a Precipitation source (concentration in precipitation water) or an Overland source (mass on the surface). In both cases, the solute can infiltrate or runoff as lateral overland flow.
Extent Type - The source can cover the entire domain (Full domain) or only part of the domain (Part domain). In both cases, the actual source strength can very spatially and temporally. The Extent is used simply to restrict the source data to a zone smaller than the model domain.
Related Items:
· Solute Transport in the Saturated Zone (V1 p. 663)
· Solute Transport in the Unsaturated Zone (V1 p. 674)
· Solute Transport in Overland Flow (V1 p. 679)