The relaxation coefficient, w, is used in the solution scheme to amplify the change in the dependent variable (hydraulic head h) during the iteration. The value of w should be less than 2 to ensure convergence but larger than 1 to accelerate the convergence.
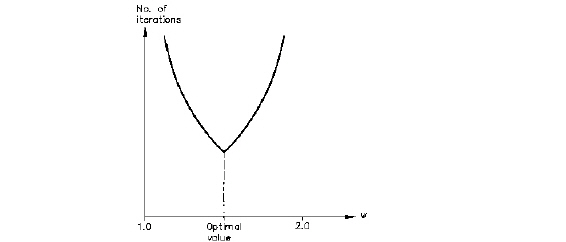
The optimal value is the value for which the minimum number of iterations are required to obtain the desired tolerance. It is a complex function of the geometry of the grid and aquifer properties. Figure 30.5 illustrates the relation between w and the number of iterations for a given grid. In practice the optimal value of w can be found after setting up the grid. The model is run for a few time steps (e.g. ten) with a range of w values between 1 and 2, and the total number of iterations is plotted for each run against the w value as shown in Figure 30.5. The minimum number of iterations corresponds to the optimal value of w.

Figure 30.5 Empirically relationship between the relaxation coefficient w and number of iterations for a given model.