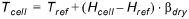
Air temperature varies linearily with elevation. Snow typically accumulates at higher elevations, but the temperature measuring network is rarely dense enough to represent the spatial variation of temperature that is known to exist in the catchment. Furthermore, the change in temperature with elevation depends on the relative humidity. Thus, the elevation corrected temperature in a cell, under dry conditions, is
and under wet conditions (when it is raining or snowing) is
where Tcell is the air temperature in the cell, Tref is the measured air temperature at a weather station, Hcell is the elevation of the cell, Href is the elevation of the weather station, and bdry and bwet are the elevation correction factors (lapse rate) for temperature under dry and wet conditions. Wet conditions are defined as any time step were the precipitation rate is greater than zero.
Note The air temperature is also used for temperature dependent decay, so the air temperature elevation correction is available whenever air temperature needs to be specified.
Note Air temperatures are specified as instantaneous values. Thus, for air temperature time series, an average air temperature is used in each time step based on a linear interpolation between two instantaneous values.