The Digital Filtering Analysis module provides different digital filter options. Basically filtering is a process of selecting, attenuating, or suppressing certain frequency components of a time series signal by a desired amount, allowing a digital filter to shape the frequency spectrum of the signal.
The Digital Filtering Analysis module uses a class of filters called Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filters also known as non-recursive filters. These filters are characterised by filter coefficients (in the time domain), which are derived from specified transfer functions in the frequency domain. The actual filter operation takes place in time domain by convoluting the input time series and the filter coefficients.
The digital filtering can be applied to data from:
· Physical model tests
· Field measurements
· Numerical simulations

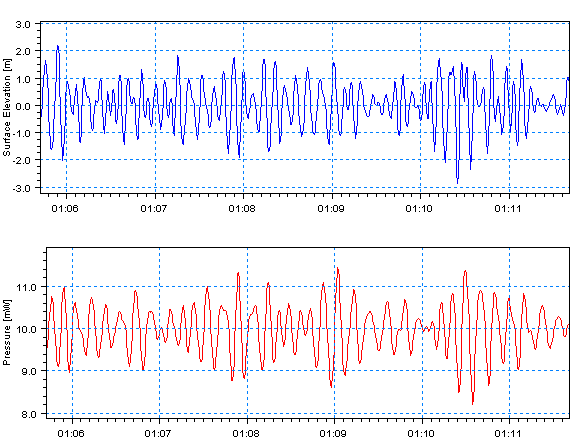
Figure 4.1 The figure shows a time series of pressure converted to a time series of surface elevation by digital filtering
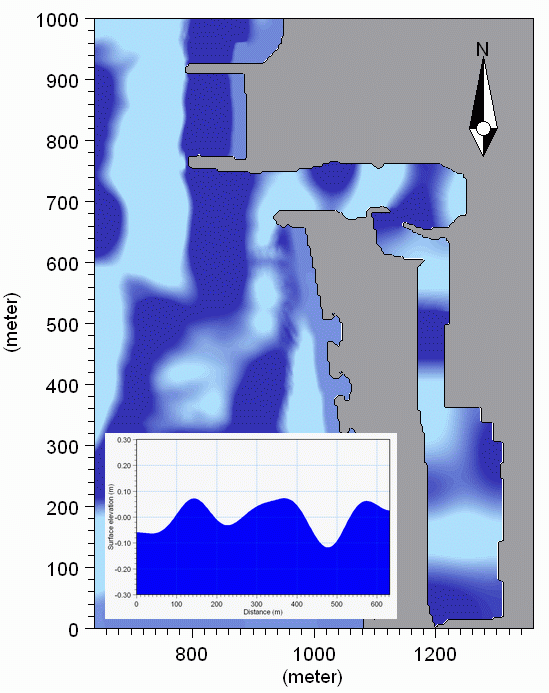
Figure 4.2 Band-pass filtered surface elevation on top of a bathymetry. A lengthwise profile of the inner harbour is inserted in the lower left corner. Input data is based on a MIKE 21 BW Boussinesq Waves simulation