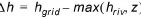
Steady-state groundwater simulations
For steady-state groundwater models, MIKE Hydro River is not actually run. Rather the initial water level in MIKE Hydro River is used for calculating da in the conductance formulas and hriv for the head gradient.
To improve numerical stability during steady-state groundwater simulations, the actual conductance used in the current iteration is an average of the currently calculated conductance and the conductance used in the previous iteration.
Canyon option for steady-state groundwater simulations
In the case of a deep, narrow channel crossing multiple model layers, the head difference used in Equations (27.1) and (27.2) can optionally be limited by the bottom elevation of the layer. Thus,
where z is the bottom of the current layer.
The above formulation reduces the infiltration from upper layers by reducing the available gradient. Without the ‘Canyon’ option, MIKE SHE effectively assumes that the river is hydraulically connected to the upper most model layer, since MIKE SHE calculates the exchange flow with all layers that intersect the river based on the difference between the river level and the water table.
Currently, this option is only available for steady-state models. It is activated by means of the boolean Extra Parameter, Enable Canyon Exchange. For more information on the use of extra parameters, see Extra Parameters (V1 p. 733).